Otitis Externa
WHAT IS IT?
Otitis externa is an infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the external ear, which is formed by the pinna (commonly known as the ear) and the external auditory canal. The outermost part of the external auditory canal is lined with thick skin that contains hair and glands that produce cerumen (commonly known as earwax) (Fig. 1)1.
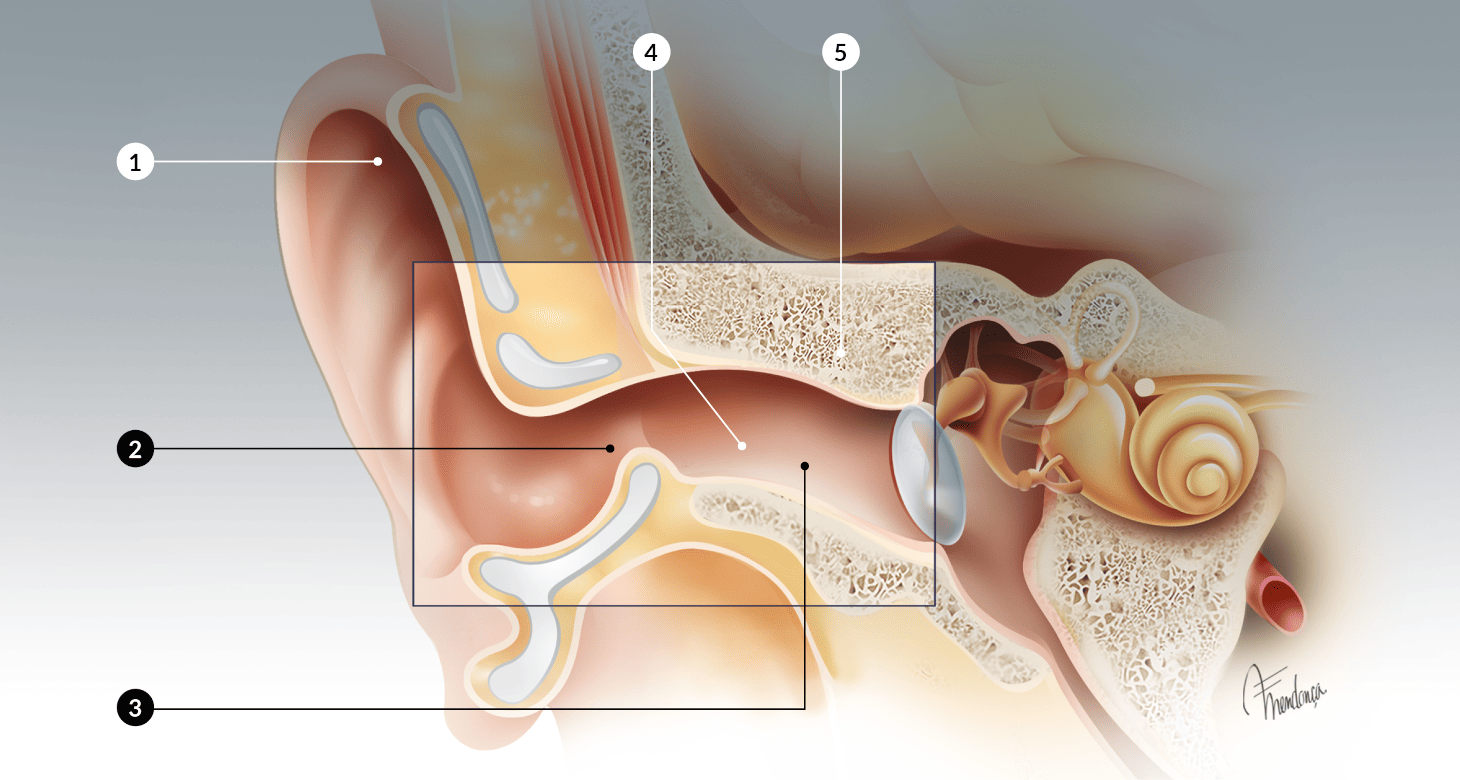
https://otosurgeryatlas.stanford.edu/otologic-surgery-atlas/surgical-anatomy-of-the-ear/
In otitis externa, the infection is usually bacterial and mainly affects the external auditory canal but can be extended to the pinna and tympanic membrane.
One in 10 people experience otitis externa in their lifetime, predominantly affecting adults, rarely pre-school children.
ARE THERE PREDISPOSING FACTORS FOR OTITIS EXTERNA?
There are several factors that predispose to the appearance of otitis externa3 (Fig. 2):
- Narrowing of the ear canal
- The presence of bone formations (exostoses and osteomas), a common situation in water sports enthusiasts
- Poor ventilation (earphones, noise muffs, hearing aids)
- Skin diseases such as eczema, psoriasis, seborrhoea
- Swimming, heat and humidity/water
- Improper handling, traumatic removal of cerumen, use of cotton buds
- Systemic illnesses (diabetes, immunosuppression)
- Irritant substances (shampoos and soaps)
- Radiation, chemotherapy
- Otitis media suppurative
- Previous surgery on the EAC
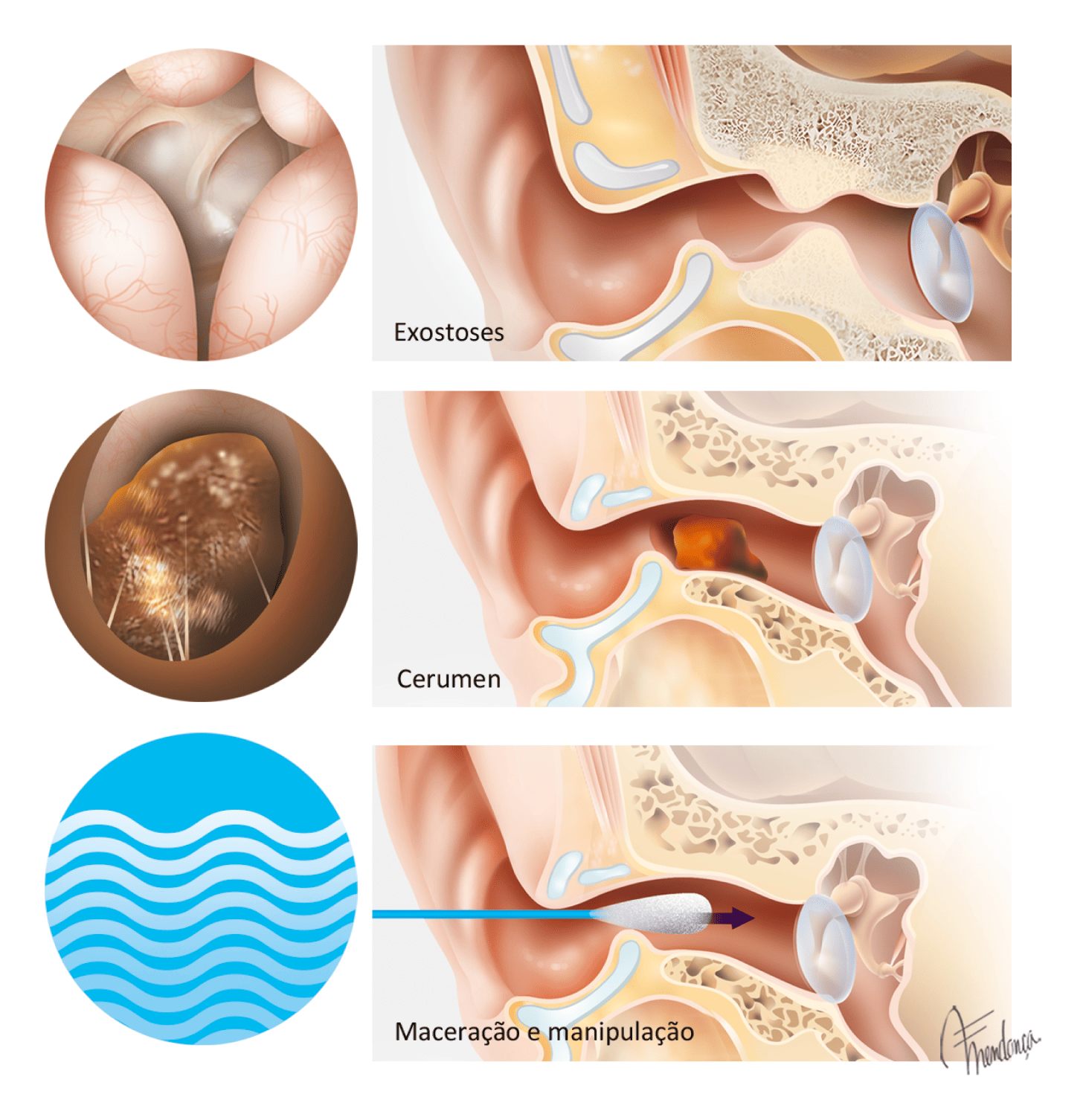
https://otosurgeryatlas.stanford.edu/otologic-surgery-atlas/surgical-anatomy-of-the-ear/
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS?
Otitis externa includes symptoms of varying intensity3:
- Pain in the ear
- Sensitivity to palpation
- Itching
- Filling sensation in the ear
- Reduced hearing
Observation usually reveals3,4 (Fig.3):
- Swelling of the ear canal with a reduction in the calibre of the canal orifice
- Sparse and thick pus
- Swelling of the pinna with enlargement of the neighbouring ganglia may occur
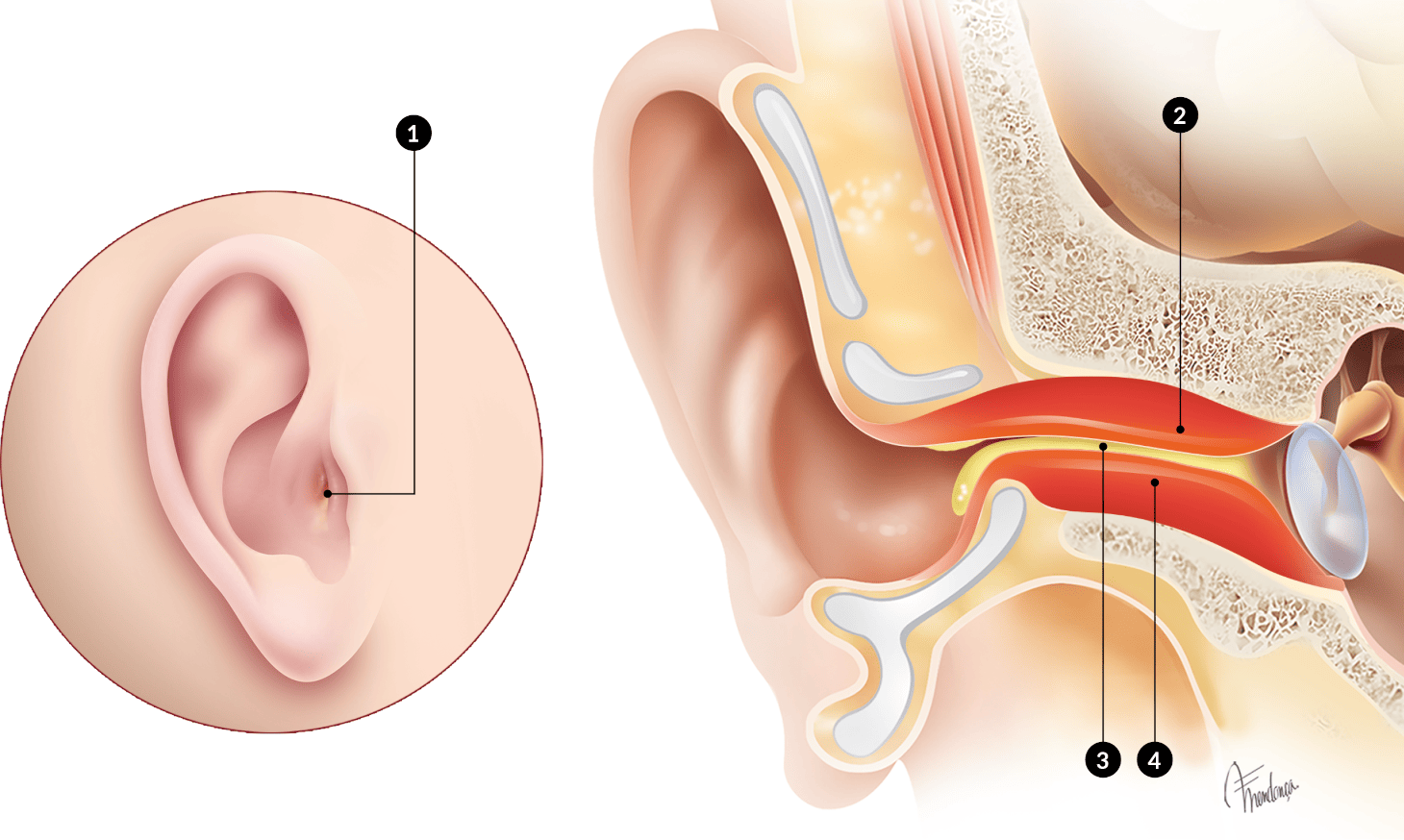
https://otosurgeryatlas.stanford.edu/otologic-surgery-atlas/surgical-anatomy-of-the-ear/
HOW IS OTITIS EXTERNA TREATED?
Bacteria predominate in otitis externa3:
- Staphilococcus aureus (11-34%)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (22-62%)
- Staphilococcus epidermidis
- Corynebacteria
Treatment is prescribed by the doctor after observation, and consists in ear drops that combine an antibiotic with a corticoid, which reduces discomfort and pain and are very effective.
Oral treatment is reserved for situations where the infection is extensive, has not been resolved with the ear drops or in patients with serious illnesses3,4.
There are several topical therapeutic alternatives3,4.
- neomycin/polymyxin B and fluocinolone
- neomycin/polymyxin B and dexamethasone
- ofloxacin and dexamethasone
- ciprofloxacin and fluocinolone
- acidification of EAC with 70° alcohol saturated with boric acid
1. Subtil,J.,Martins, N - Anatomia e fisiologia do ouvido médio e externo, in Audiologia, Som e Audição-das bases à Clínica Coordenadores João Subtil, Luisa Monteiro, Edição Círculo Médico, 2018.
2. Dr. Jackler and Ms. Gralapp https://otosurgeryatlas.stanford.edu/otologic-surgery-atlas/surgical-anatomy-of-the-ear/ consultado em 16-11-23
3. Otitis Externa. Investigation and Evidence-Based Treatment. Susanne Wiegand, Reinhard Berner, Antonius Schneider, Ellen Lundershausen, Andreas DietzDtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Mar; 116(13): 224–234. Published online 2019 Mar 29. doi: 10.3238/ arztebl.2019.0224PMCID: PMC6522672
4. Otitis Externa. Yiraima Medina-Blasini; Tariq Sharman, August 7, 2021. Continuing Education Activity, StatPearls (Internet), NCBI Resources
